Accelerating statistical data sharing with SDMX and intuitive data portals

Access to accurate statistical information is key to the successful functioning of the global economy and for policymakers and businesses to make informed decisions around subjects that impact us all. How can institutions effectively and efficiently share their statistical data in an interoperable, scalable way to democratize access and build trust?
Statistical data, such as economic, finance and trade information, is essential to understanding the global economy. From inflation and interest rates to unemployment and growth figures, it influences and informs all of our lives, while providing the foundation for decision-making by elected politicians and public employees at a local, national and international level. Clear, understandable statistics enable the media and citizens to hold their elected officials to account while feeding into investment decisions by businesses across the world.
All of this means that statistics have to be trustworthy and easy to compare globally. However, given the complexity of the field this can be difficult, particularly if different organizations use their own formats and ways of describing data. That’s why the Statistical Data and Metadata eXchange (SDMX) standard has been created – this blog explains what it is, the benefits it delivers and how it combines with data portals to deliver seamless statistical data sharing.
Understanding the challenges of statistical data sharing
Government and public sector organizations at a national and international level are producing increasing volumes of statistical data, measuring a huge range of areas from financial flows to industrial and agricultural production figures. This is vital to understanding the economic world around us and enabling informed decision-making, research, and transparency, particularly when sharing and comparing data from multiple organizations and between countries.
However, traditionally different organizations created their own standards and formats when it came to statistical data, built around their own specific requirements. While this enabled internal analysis of figures within an organization, it created a challenge if this data was being shared externally with other bodies, particularly on an international basis. How particular statistics were measured and described could be subtly different, leading to:
- Inaccuracies if different statistical data was combined, potentially leading to poor decision-making
- An inability to meaningfully compare different data assets that cover the same area
- Inefficiency as data had to be manually reformatted and checked prior to sharing or usage
- A lack of transparency and trust in data, further impacting its use and even potentially undermining faith in public bodies by citizens and the media
Introducing SDMX
To overcome these challenges the SDMX standard was created and launched in 2002, becoming an ISO standard in 2004. It was sponsored by eight major international organizations involved in statistical data:
- The Bank for International Settlements (BIS)
- European Central Bank (ECB)
- Eurostat (Statistical Office of the European Union)
- International Labour Organization (ILO)
- International Monetary Fund (IMF)
- Organisation for Economic Cooperation and Development (OECD)
- United Nations Statistical Division (UNSD)
- World Bank
The aim of SDMX is to provide a common framework, standard and tools to standardize the exchange of statistical data and metadata. between international organizations and countries, increasing harmonization, efficiency and communication.
As can be seen by the different sponsors involved, SDMX is designed to comprehensively cover all types of statistical data, including information around agriculture, economics, finance, trade, the environment, the UN Sustainable Development Goals and social statistics.
Since its launch it has been adopted globally by a range of countries and organizations, all of whom make data available in the SDMX format to aid interoperability and transparency. The standard is maintained by the SDMX initiative, an active international community that helps increase adoption of SDMX.
The benefits of SDMX
SDMX provides nine key benefits for producers and consumers of statistics data:
- Harmonization of statistical data and metadata, delivering consistency and building trust that data is consistent and high-quality
- Greater efficiency as data preparation, sharing and reporting can be automated by following its standards and guidelines
- Better informed policy-setting and decision-making as data is consistent and comparable between organizations and countries
- Reduced costs for data consumers and businesses creating applications to access statistical data
- Lower development and maintenance costs for data producers and consumers through standardization
- Faster publication of data through automation
- Improved data quality through better and faster validation
- Simpler open data sharing, removing barriers to data access and democratizing the sharing of statistical data
- Improved data governance by setting and enforcing standards at an international and organizational level
Since the introduction of SDMX, a global community of practitioners and ecosystem of tools and learning resources has developed, with regular conferences and workshops being held across the globe. This increases collaboration between statistical data providers and consumers, and helps modernize and digitalize the profession.
The technology behind SDMX
SDMX is made up of three components:
- Technical standards (including its Information Model)
- Statistical guidelines
- An IT architecture and tools
The SDMX information model and statistical guidelines describe statistical data and metadata in a consistent, harmonized manner to ensure interoperability. This is then exchanged through a set of common IT tools, processes, terminologies, and methodologies that make information flow between data producers and consumers seamless and automated.
Data can be exchanged through different formats within SDMX:
- SDMX-ML, used for the exchange of structural metadata, data sets and queries
- SDMX-EDI (GESMES/TS), used by the European Central Bank to exchange statistical data and metadata with central banks in European countries
- SDMX-JSON, to support data sharing over the internet
The uses of SDMX
SDMX delivers value when used in two specific ways.
Firstly, it underpins data exchange between different statistical organizations, improving the harmonized collection and sharing process of both data and metadata. It enables processes to be fully automated, increasing efficiency, while guaranteeing quality and consistency.
Secondly, statistical organizations can use SDMX to make data easily available to data consumers via their portals through data discovery and visualization. When a user searches for specific data or accesses a page, relevant data and metadata is retrieved from SDMX structural repositories and then transformed into visualizations such as tables, graphs, or charts.
Delivering seamless sharing of statistical data
Clearly SDMX is a major step forward in sharing statistical data – however, while it handles technical interoperability and compatibility, this is only part of the puzzle when it comes to effectively sharing data. To ensure data consumers of all types can discover, interact with and reuse data confidently, organizations need to make this information available via internal and external data portals and data marketplaces. These solutions seamlessly connect users to the data they require through an e-commerce style interface and intuitive user experience that builds trust that they are accessing the most relevant data for their needs, and that they understand exactly what it covers.
Opendatasoft and SDMX
Following 10 months of research and development, Opendatasoft has integrated the SDMX standard into its data portal solution, enabling players in the statistics community to easily share relevant data and metadata in a standardized, automated format. Working closely with customer Banque de France, the French central bank, the feature has been comprehensively tested and is now integrated into Opendatasoft’s indexing and search capabilities, enabling the publication and sharing of statistical data at scale. This innovation makes Opendatasoft the partner of choice for organizations and institutions in the SDMX community looking to create effective, intuitive data portals.
Banque de France
Banque de France shares statistical data through Webstat, its new Opendatasoft-based statistical data portal. Replacing the bank’s previous portal, the new Webstat provides visitors with a modernized interface and a better user experience for data discovery and consumption. Just as on an e-commerce website, data assets can be favorited and added to a visitor’s shopping basket to make them easy to retrieve and compare.
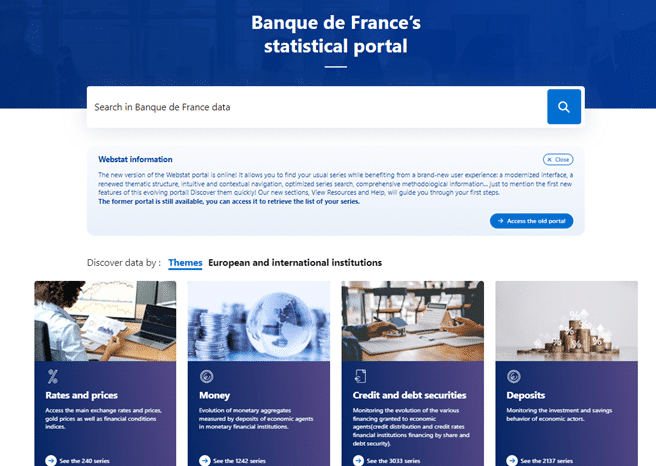
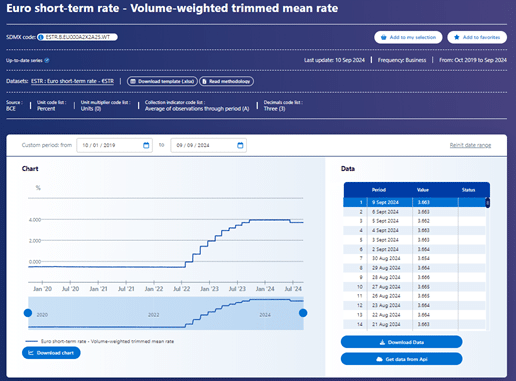
Since its launch in July 2024, Webstat has provided users with access to more than 45,000 datasets, available via the SDMX information standard, offering a more intuitive and seamless user journey, an updated theme-based structure, intuitive and contextual navigation, and an optimized search engine. All of this is backed by comprehensive resources and help to enable all types of user, from policymakers and researchers to journalists and citizens, to quickly and confidently find the information they are looking for.
Statistical data is essential to the smooth running of the global economy – making it freely available to all is vital to collaboration, decision-making and transparency, enabling citizens to hold their elected governments to account. The combination of the SDMX standard and intuitive, user-friendly data portals ensure that statistical data is interoperable, understandable and delivered efficiently, building trust and accelerating data democratization.
Want to learn more about the different data formats that Opendatasoft supports? Contact us to book a tailored demo with our experts!

Understanding the importance of metadata and putting the right strategy in place is vital to effective data sharing and reuse via data portals to progress towards data democratization. Our comprehensive blog explains what metadata is, outlines its benefits and shares best practice for your strategy.
Well-structured metadata is crucial to enabling data to be found and used with confidence within organizations and ecosystems. It is central to effective data sharing and reuse. At Opendatasoft our mission is to accelerate data democratization, ensuring that everyone has access to easily understandable information in their working and home lives. Our data portal solution enables data democratization by centralizing all of an organization’s data assets and making it available to all internal and external users in a seamless, intuitive way, without requiring specialist skills or support.