Data discovery – the ultimate guide

Data discovery is an essential part of turning data into business value at scale. Our in-depth blog explains exactly what data discovery covers and how to implement it, sharing best practice to help organizations successfully industrialize their data sharing programs and meet the needs of internal and external users.
Organizations today have access to enormous – and growing – volumes of data from a variety of sources. Whether generated internally by business systems, customers, or Internet of Things sensor networks, or externally by partners within their ecosystems, companies need to turn this raw data into useful data intelligence and insights to ensure competitiveness and to achieve their objectives.
This is why data discovery is vital to unlocking the value that data provides, enabling organizations to make sense of their information and users to successfully understand and harness it within their daily working lives.
What is data discovery?
Data discovery is a multi-stage process that covers the entire data lifecycle. It begins with finding and classifying data from different sources across the organization, and then making it easily available for all to use. It can be carried out manually or automated using data discovery tools.
The benefits of data discovery
A robust data discovery strategy delivers six key benefits:
- Businesses have a complete view of their data from across the organization
- Data can be checked and validated to ensure that it is reliable and high-quality
- It is an essential part of data governance, giving confidence in data assets
- Data discovery ensures compliance with regulations (such as the GDPR and CCPA), as well as enabling better management of risk
- By providing a full picture of the data landscape, data discovery improves efficiency, removes duplication and optimizes processes
- By making data discoverable by everyone, organizations improve decision-making, increase transparency with stakeholders, make it easy to create insights from data, and build a data-driven culture
The four stages of data discovery
While the data discovery process has different steps, these can be essentially distilled into four distinct stages:
Collection and preparation
First, businesses need to collect data from across the organization. This starts by gaining visibility of the information that is being generated to give a complete picture of the data landscape. Relevant data should then be collected through data pipelines and prepared to ensure that it is high-quality, meets governance standards, and is consistent with other, existing datasets in terms of format.
Often collecting data requires organizations to break down silos between departments to gain access to information, which requires a collaborative approach that educates data owners about the value that data can provide to the wider business.
Once collected, preparation includes cleaning data (to remove errors and outliers or to standardize formats), potentially enriching it with other internal or external data and ensuring that it is described accurately through comprehensive metadata. Data enrichment, such as by adding geographic or public demographic information helps with usability and ultimately makes it easier for end-users to understand.
Opendatasoft’s platform makes collecting and preparing data seamless, whatever its source. It included connectors to popular business applications and cloud storage solutions, as well as public data sources available through the Opendatasoft Data hub. Powerful processors automate data preparation, while built-in metadata templates help create high quality data assets that can be easily cataloged and discovered.
Visualization and availability
Once data is standardized and prepared it needs to be made available to users in ways that fit with their requirements and that are easily accessible, such as through a central data portal.
As most people are not data specialists they struggle to make sense of raw, tabular data. Instead, they want to be able to interact with the data through compelling visualizations that bring information to life in an understandable, accessible way. Opendatasoft’s platform makes it easy for users to discover data in the right format, by enabling the creation of data visualizations, as tabular datasets and via APIs.
Data visualizations include:
- Maps that plot information across a geographic area, allowing users to zoom in and out to get more detail on specific data points, such as a location.
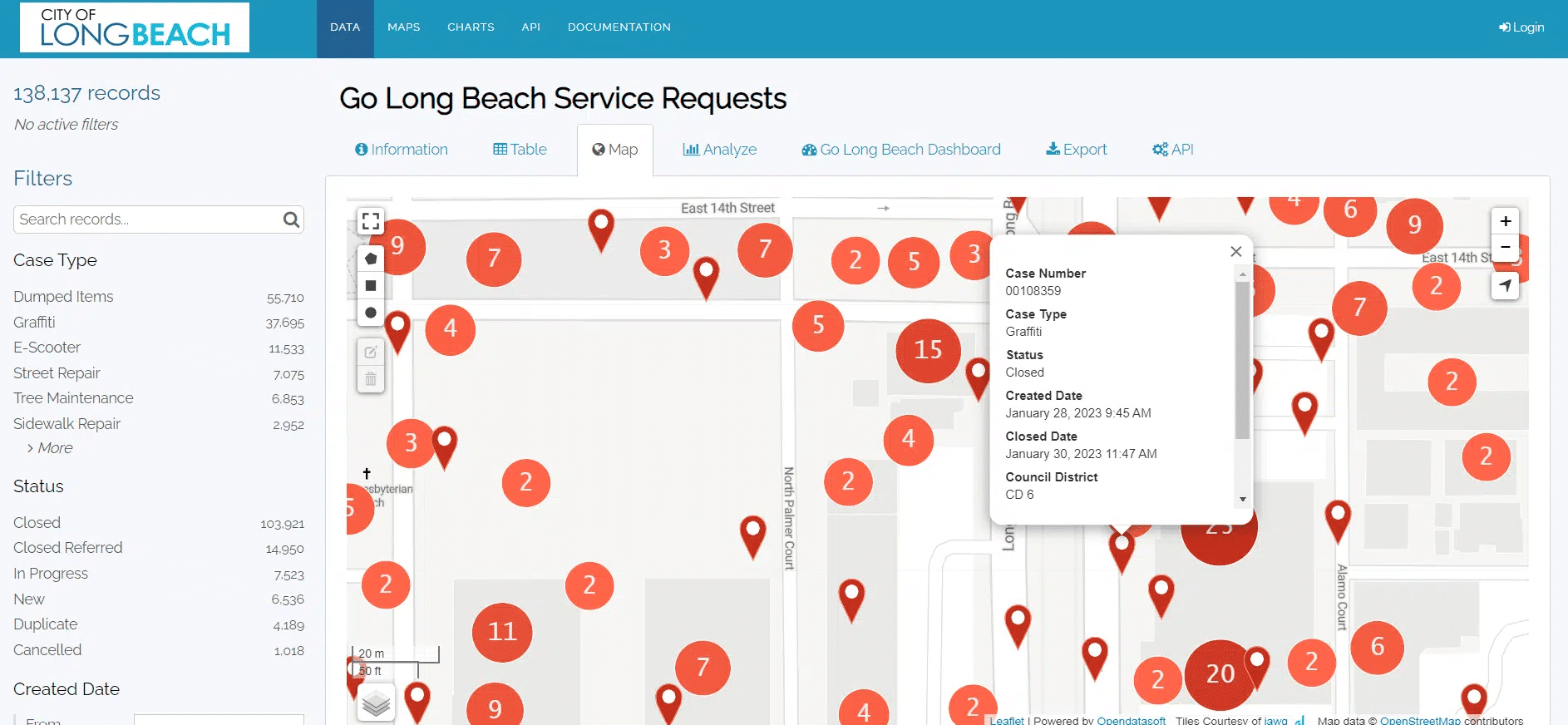
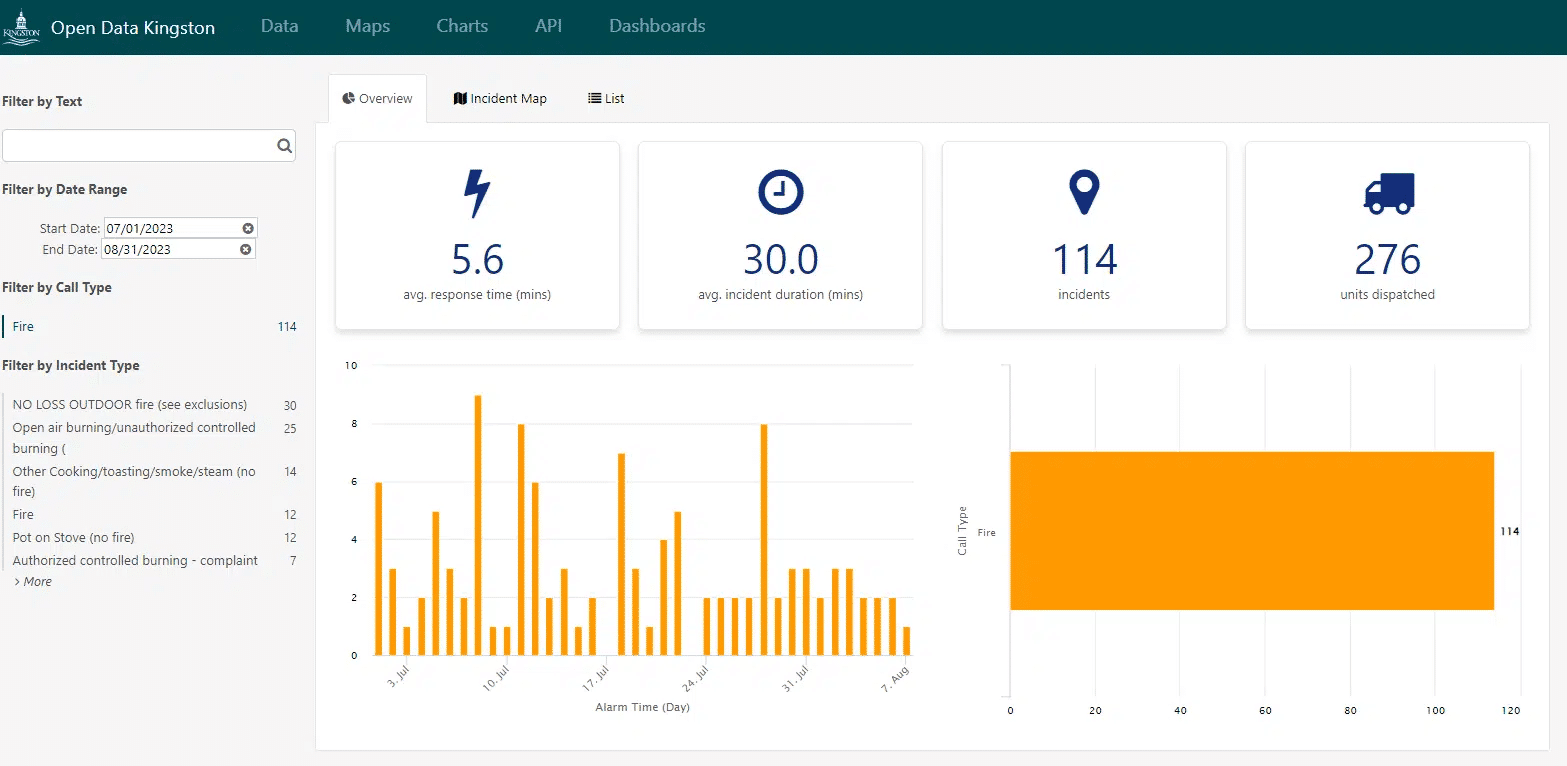
- Interactive dashboards that bring together data from multiple sources to provide a clear view of key metrics, such as energy usage or sales volumes. This should allow the user to drill-down to get further detail and to easily query data without needing in-depth data skills
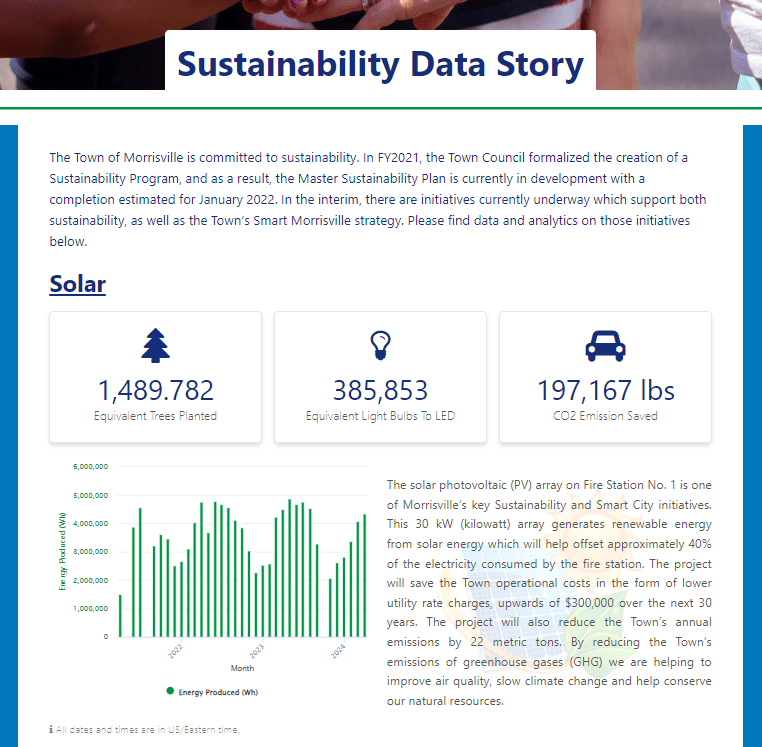
- Data stories that combine text, data and graphics to provide a comprehensive view of a theme or area. For example, many public sector organizations have created sustainability data stories on their data portals, demonstrating their progress against environmental targets
Making data easily discoverable
Ensuring data is discoverable is crucial – many users will not know exactly what information an organization offers, making the process of finding data and enabling them to access it with confidence central to success. Centralizing data in a single portal, whether internal, external or for partners, brings together information so that it can be easily accessed. This goes beyond static data catalogs by allowing users to locate, explore and access data assets. Navigation, user interface and search must be seamless to ensure that everyone can find relevant data assets through the portal. It has to be simple to explore data, understand what it covers and navigate between data assets. Essentially the overall experience must be as intuitive as any internet search engine to ensure assets are found and used.
Analysis and reporting
The final stage of data discovery is its use for analysis and reporting. This could be through employees accessing data assets and using them to make their daily working lives easier and more productive, managers taking decisions based on information shared on dashboards, or citizens better understanding a municipality’s performance and spending by reading a data story. Opendatasoft’s data lineage feature helps understand how different data assets are being used, and who is using them, providing in-depth reporting that can be used to improve overall data discovery.
Analysis and reporting requires a combination of the right data being available in the right formats – and also education to ensure that users are confident in harnessing data without requiring support from data specialists. Only then will organizations build a data-driven culture that democratizes access to information to benefit everyone.
Understanding data discovery best practice
Data discovery is essential to turning data into value – without it organizations will simply not be able to industrialize data use internally and externally. Achieving success requires businesses to focus on these best practices:
Automate the process
Rather than time-consuming manual data discovery, organizations should embrace tools that automate the process, helping to first locate data and then manage the data pipeline to prepare and share it.
Create a single one-stop shop for data
Users need to know where they can find all relevant data from across the organization. Businesses therefore need to centralize data from different departments in a single data portal that is available to everyone, creating a well-signposted one-stop shop for all information and data assets.
Focus on the user experience
Make it easy for users to find and interact with data assets through an intuitive experience that everyone can understand and access without requiring specialist training. Base your portal on the same user experience as an e-commerce style marketplace, with full support, documentation and seamless design to encourage usage and make it easy to find relevant data.
Build a data culture
Many non-specialists inside and outside organizations can be wary about using data in their working and daily lives. Educate them about the importance of data and show them how easy it is to use, building a data culture that underpins data democratization.
Make creating data visualizations simple and straightforward
Often building reports and dashboards is a complex, time-consuming process that requires specialist data and design skills. Choose a platform that enables you to create visualizations through no code/drag and drop options to make it simpler for non-specialists to build visualizations to aid data discovery.
Aid discovery through powerful, AI-driven search
Given the number of data assets available on many portals, it can be difficult for users to find the exact match for their requirements. Use AI-powered semantic search to improve the accuracy of results, including providing recommendations for other, relevant datasets that may be of interest.
Enforce strong data governance and metadata processes
Poor quality or badly described data won’t give users confidence, which means they simply will not rely on it, harming data democratization. Therefore put in place strong data governance processes to ensure quality and standardized metadata to help with the discovery process.
Understand usage and improve through data lineage
Data discovery is a continuous process. Monitor which data assets are most popular and deploy data lineage tools to understand where they are being used downstream in particular applications. This will help focus your efforts and streamline maintenance and management.
The role of data portals within data discovery
Data portals connect users to relevant data, making them essential to effective data discovery and data management strategies. They provide the ‘last mile’ of the data pipeline, giving users the right data, in the right format, in ways that they can easily understand and work with.
It is vital that portals are seamless and easy to use by non-data specialists, with an intuitive interface, clear navigation, multiple visualizations and tailored experiences for different groups of stakeholders. Data portals need to bring the same level of discoverability to data as on an e-commerce marketplace site if information is to be found, understood and used by all. Data must be easy to find through AI-powered search, with an in-depth explanation of what it covers, and the ability to automatically recommend other relevant data assets as well as enabling users to directly contact data owners with their feedback and queries.
It can be hard to understand exactly what a data product is, given the many ways that the term is defined and applied. To provide clarity this article provides a business-focused definition of a data product, centered on how it makes data accessible and usable by the wider organization, while creating long-term business value.