Driving forward data sharing in the energy sector
How can energy and utility companies successfully share their increasing volumes of data with all stakeholders to help deliver on net zero goals? Our Energy User Club brought together leading utilities to discuss best practice around scaling data sharing and value.
Data sharing is increasingly vital to companies operating in the energy and utility sector. Providing easy access to information for internal employees and external stakeholders, such as local authorities, generators and customers, is essential to increase collaboration, improve efficiency, meet regulatory needs, and support the transition to net zero.
Utilities across the globe face the same challenges when it comes to effectively sharing data, with a growing number deploying Opendatasoft’s data product marketplace solution at the center of their strategies. To enable clients to share best practice and learn from each other, Opendatasoft recently organized its first Energy User Club meeting. Bringing together participants from across Europe, it provided a forum to swap ideas, understand Opendatasoft’s product roadmap, and work together to drive forward data sharing in the energy sector. This blog highlights some of the key points from the discussion.
Three key objectives for utility data sharing
During the event representatives from E-REDES (Portugal), Northern Powergrid and UK Power Networks (both UK) shared their experiences, leading discussions and providing inspiration to their peers. Their presentations highlighted three key themes that are central to success – delivering a customized stakeholder experience, driving greater data usage, and involving the wider organization in data projects.
Delivering a customized stakeholder experience
Utilities now have to communicate and collaborate with an ever-growing range of stakeholders in order to help create an effective, decarbonized power grid. As well as traditional stakeholders such as power generating companies and regulators, they now need to work with groups such as local authorities, researchers, operators of EV charging stations, and, of course, citizens.
Often these groups are not energy specialists, meaning they don’t necessarily understand industry-specific terms or definitions. Equally, many are not data specialists either, and want to be able to access information in more understandable formats compared to raw, tabular data.
All of this means that energy data portals have to make it easy for specific stakeholder groups to discover, access and use relevant data through an intuitive, tailored, self-service experience. Simply publishing data on a portal is not enough.
For example, E-REDES is the principal operator of mainland Portugal’s high, medium and low voltage electricity distribution networks, transmitting power via its 245,000km energy grid to its 6.4 million customers. It knew that its data portal had to meet the specific needs of its audiences, so it delivers a customized experience, with data organized by theme and usage profile, allowing tailored navigation for specific groups and accelerating access to relevant data.
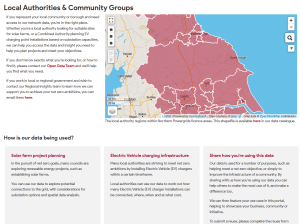
Working with municipalities
One of the key stakeholders for energy data are local authorities/municipalities. They need to be able to understand current usage and their existing and future local energy landscape in order to plan activities to increase energy efficiency and enable decarbonization. This covers everything from showing their decarbonization progress compared to others, highlighting areas which require additional support for energy efficiency and where renewable generation capacity or EV charging stations can be sited.
To meet this need, E-REDES spoke extensively to Portuguese municipalities before launching its portal, using this feedback to create a specific drill-down municipality dashboard. Staff and citizens can find their municipality by searching by name or via a clickable map and then access local metrics on areas such as monthly consumption, renewable generation, public EV charging points and planned/actual energy interruptions. Through visualizations users can see how specific municipalities compare to others and change over time, delivering transparency and enabling municipal staff to focus on making better-informed decisions to drive the energy transition.
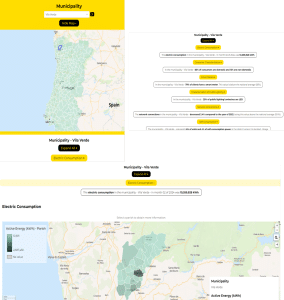
In the UK, Northern Powergrid (NPG) is a distribution network operator (DNO) that serves 3.9 million homes and businesses across the North East, Yorkshire and northern Lincolnshire. It works with 33 local authorities within its region and provides them with all relevant data via a single, specific page. This includes examples and use cases of how other local authorities are using this data, as well as highlighting relevant datasets and pages. By using Opendatasoft’s processor for local authority boundaries, NPG is able to automatically add these fields to key datasets, enabling information to be quickly filtered by users. Different datasets are also brought together and shared through a single dashboard, giving local authorities a single view of all relevant information, rather than needing to move between tabs.
Driving usage and collaboration
Publishing energy data is just the start point to drive its usage. Success requires utilities to carry out proactive outreach with different stakeholder groups, listening to their needs, providing hands-on tutorials and keeping them up-to-date with progress on new datasets.
Data must also be provided in ways that users can easily understand and work with. This could be through a dashboard or other map-based visualization for non-specialists, or via APIs for more technical users. As well as an intuitive user interface, Northern Powergrid has invested in “how to” tutorial videos on its portal, as well as carrying out extensive research to fine-tune the experience and deliver specific pages and data assets. It also runs regular webinars to update its community on new features and innovations. UK Power Networks, responsible for power distribution to homes and businesses across London, East Anglia and the South East, has created structured user journeys around different needs, with tailored visualizations that deliver useful, effective information to stakeholders.
E-REDES extensively promotes its portal, attending energy/municipality conferences and events and appearing in more than 70 media articles and interviews. It has also carried out a roadshow to 27 universities across the country, with a particular focus on its Open Data Academy Challenge Award. This rewards dissertations and master’s projects that focus on the theme of the energy transition and that use data from its portal as a source for research, providing monetary prizes to the three best projects, inspiring innovation and new ideas.
All of these initiatives help increase the usage of utility data by all stakeholders, enabling greater collaboration and a focus on working together to drive decarbonization. It also delivers efficiency benefits. By publishing data, such as around available capacity within substations on the portal, stakeholders (such as EV charging point operators) can access information themselves through self-service and plan where to locate new infrastructure. This reduces the number of incoming requests to the utility as initial research is all carried out on the portal, saving time for everyone involved.
Involving the wider organization in data projects
As in most organizations, data in utilities comes from a wide variety of sources and departments across the business. Additionally, central data teams are responsible for a growing range of activities, often with relatively few resources. This means that data sharing programs need to focus on two areas:
- Automating as much administration as possible around the portal to free up staff time
- Collaborating internally with data owners, helping them to publish and share their data
Building a community of data owners has multiple benefits. It provides additional resources and capabilities to the portal, as well as delivering new data products and data assets that meet specific user needs. These are designed using templates and centrally-created data contracts to ensure standardization and minimize the need for rework, enabling data owners to focus on creating and supporting data products over the longer-term.
Additionally, as data owners are closest to their data, they are best placed to help users, such as by answering their questions and incorporating their feedback moving forward. This approach enables data sharing to scale, without requiring additional central resources, while the portal still enforces key compliance processes, such as around data governance.
In the case of UK Power Networks, it works with internal teams in areas such as streetworks, connections and asset management, supporting them to share their data and meet external stakeholder needs. This ensures that available data continues to grow, helping scale data usage and value.
The data-driven energy ecosystem
Across the energy sector, utilities and other players understand the need to transform in order to meet changing needs around decarbonization, greater efficiency, and digitalization. Data is central to this transformation, providing the ability to collaborate internally and externally with a growing range of stakeholders, and help move the whole ecosystem forward. As the discussions and conversations at the first Opendatasoft Energy User Club demonstrated, utilities across the world face the same range of challenges and opportunities when it comes to data sharing. To deliver value and scale their data use they are therefore adopting and extending user-friendly, self-service data portals and data marketplaces which connect all stakeholders to the right data through tailored experiences built around their needs. Together, this will create a flexible, decarbonized energy ecosystem able to deliver on everyone’s current and future requirements.



