Everything you need to know about data enrichment
Data enrichment is essential to turning your raw data into valuable information that can be easily understood and used internally and externally. Our blog explains how to successfully implement data enrichment in your organization in order to improve quality, consistency, and standardization to maximize value.

Much of the raw data that organizations generate is often difficult to use in its original format, particularly if it is being shared outside the team that created it. For example, it might not meet governance requirements around accuracy, completeness, reliability, timeliness or consistency/standardization. All of this impacts its quality, leading to errors that prevent its widespread understanding and usage, dramatically reducing its value.
Data enrichment overcomes this challenge, ensuring that data is high quality, trusted and adding value, such as by cross-referencing it with other data sources. What is data enrichment and how do you incorporate it into your data initiatives? This blog explains how to enrich your data and maximize its value.
Making data usable at scale through data enrichment
The data trust gap
Organizations are now producing and accessing more and more data. However, data on its own does not create value – it is only when it is shared, understood, and reused that it maximizes its impact.
At its basic level raw data can simply be a table of figures that lacks context. This makes it difficult for non-specialists to understand what figures refer to, what the frequency of collection is, and how it relates to other datasets.
This leads to four issues:
- A lack of trust in the data which prevents usage
- A lack of context which makes data harder to understand
- Poor data governance, leading to inconsistencies and inefficiencies
- Potential compliance issues as confidentiality is not respected
Bridging this gap requires organizations to improve data quality and make it easier to understand through data enrichment tools and data enrichment services. Defined simply, data enrichment is a data management process that improves the quality of existing data by adding more information.
The benefits of data enrichment
Enriched data delivers a wide range of key benefits:
- Better informed decision-making as employees understand exactly what the data covers and what it means to them
- Greater use of data beyond specialists, as people trust data assets and feel confident in using them as part of their working lives
- More detailed customer knowledge, as data can be cross-referenced to provide a more complete picture of customer requirements, all while respecting confidentiality and ensuring regulatory compliance
- The ability to create new data products and services, generating new internal innovations and potential new revenue streams with existing and future customers
- More efficient operations, as data is automatically enhanced, without the need for manual intervention, saving time and resources
- Reduced errors/duplication, as data is cross-referenced and checked to highlight and correct errors and remove any duplicate data, saving on storage costs
Successfully implementing data enrichment
Improving data assets through data enrichment
Data enrichment enhances data assets by adding new information that corrects errors, adds context and ensures compliance:
Error correction
Data enrichment corrects common errors and standardizes data formats by applying automatic processors during the enrichment stage. This includes ensuring that fields, such as addresses and dates, are formatted consistently so that they meet corporate governance rules and ISO standards. For example, organizations can ensure that dates are all written in the same US or UK format or that first and second names are always in the right order. As well as meeting governance standards, processors save time, especially by automatically recognizing what a field type (such as an order value) should contain, and correcting or flagging any discrepancies.
Adding context
Raw data can be hard to understand, especially for non-specialists. Enriching data with more information, such as geographic locations, adds context and helps deepen understanding and aids the creation of compelling visualizations. Cross-referencing and adding external data (such as national zip code databases or approved business classifications) also ensures standardization, both for internal use and when sharing data externally.
Ensuring compliance
Data needs to be kept securely protected, with confidential information kept safe at all times from unauthorized access. Data enrichment therefore helps with compliance, as processors can be used to automatically anonymize specific data fields, such as locations, if they are sensitive. This not only protects information, but also meets regulatory obligations and safeguards corporate reputation.
How to deliver data enrichment
Data enrichment is a key part of the data pipeline, following on from the ingestion/collection stage. Once enriched, data is then stored or made available via tools such as data portals or data warehouses.
Data enrichment can be achieved in two ways, by using internal or external data:
Using internal sources for data enrichment
Cross-referencing against internal data sources is especially important for data governance and meeting corporate standards. Essentially, by applying the same processes and formatting to all data, organizations ensure consistency and that everyone understands what a dataset or a field within it refers to.
Cross-referencing multiple, similar datasets also enables organizations to triangulate analysis and draw more in-depth, reliable conclusions. For example, by enriching the information in your CRM with sales data you can actually show which of your products actually generates the highest profits when costs are subtracted from revenues.
Enriching data with internal information adds value, builds trust and ensures that there is a single version of the truth, both across different departments and externally when working with partners.
For example, electricity distribution company UK Power Networks works closely with local authorities to help them transition to net zero when planning their future local energy needs.
As part of this it has created a dedicated Local Area Energy Planning (LAEP) page that provides access to a range of its datasets enriched with further information from a range of sources to aid understanding. Built on 153 datasets, the page is set out under six common data themes identified by local authorities including energy generation, land use and environment, heat and buildings, and mobility. Users can click through to explore 30 relevant use cases, such as the best places to site new EV charging facilities or network constraints that might impact renewable projects.
Using external sources for data enrichment
Enriching datasets with external/third-party information delivers a range of benefits. At a basic level it enables the standardization of data (such as through ISO standards), ensuring consistency with widely-used and recognized formats. It deepens understanding, such as by adding location or weather information to give greater context and make data easier to visualize.
It also increases efficiency, as there is no need to create and maintain your own data sources if they are available externally. For example, governments and third-parties maintain directories of registered company names, which can be cross-referenced to enrich your own data assets.
There is a huge, and growing, range of external data sources that are now available, including:
- Official government data (census data, databases of company registrations and activity/finances, electoral/municipal/state and country boundaries)
- Geospatial data (weather, temperature, mapping)
- Business data (such as credit checking information)
- Partner data (such as around sales or product usage)
- Social media data (customer reviews of a product, for example)
Some of this external data is freely available, as open data, such as from public sector bodies, while other sources are collected and sold by specialist companies. For example, the Opendatasoft Data Hub is a free catalog of over 33,000 datasets and reference data that has been collected and checked by our team, helping organizations to enrich their assets and achieve their objectives more quickly.
Our blog, Unleashing the full value of your data by enriching it with external data explains more about the specific benefits of applying external data to your data assets.
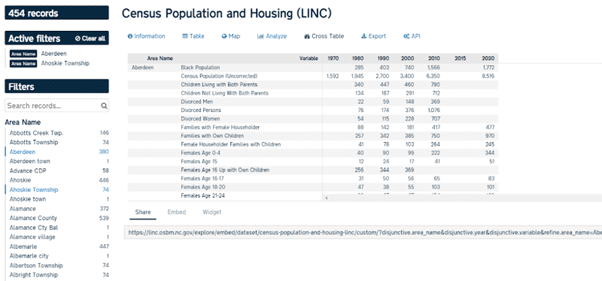
North Carolina’s Office of State Budget and Management (OSBM) collects and makes available enormous volumes of statistical data from across 20 state departments and federal agencies on its LINC portal. This covers areas as diverse as population (including census data), labor force, education and agriculture. It uses information such as census data to enrich its own data assets, giving them extra depth and enabling users, such as local elected officials, to benefit from a more complete view of their county or municipality.
Effectively sharing enriched data
Data enrichment is a key step in maximizing value from an organization’s data assets. It provides the foundation for effective data sharing by improving the quality, accuracy and usability of data.
To deliver full value from enriched data, it has to be made seamlessly available to all relevant users via an intuitive data portal. This increases sharing by providing access to a full range of data assets, backed up by clear context, metadata and explanations of what the dataset covers to build trust and user confidence. An effective data portal allows users to experience data through enriched visualizations, such as maps, data stories containing multiple data sources, or interactive dashboards, as well as enabling them to combine different datasets themselves to create their own visualizations. This all helps increase usage and maximizes the value of your data.
Want to learn how to enrich your data and deliver it via an intuitive data portal? Book a demo of our solution to find out more!



