Analytics
The objective of analytics is to help organizations make better decisions. This enables them to remain competitive, increase sales, acquire new customers, better engage with stakeholders and create new services.
What is analytics?
Analytics covers the analysis of data in its broadest sense, including its collection, measurement, analysis, visualization and interpretation. The objective is to help organizations make better decisions.
Analytics can involve the analysis of data from a variety of sources:
- Websites (customer behavior, website performance etc) (web analytics)
- Social networks (user behavior)
- Mobile apps (user behavior/movement data)
- Business systems (ERP, sales, CRM)
- Customer service feedback
- Reports and analysis (e.g. government reports)
- Demographic data
- Other third-party datasets
Analytics can be implemented by all types of organizations, regardless of their size or sector of activity. Every organization can use data to improve their business performance, optimize the user experience, improve operational processes, and increase return on investment, for example.
Data analytics vs data science
With the development of big data, data experts are multiplying. It is therefore common to meet data analysts and data scientists. The major difference is that data science is predictive – it involves analyzing large data sets in order to identify new concepts and hidden relationships. On the other hand, data analytics is reactive – it is always based on data that already exists.
The 3 categories of analytics
Analytics can be divided into different categories depending on the application:
- Exploratory Data Analysis (EDA): it is about exploring the data and drawing conclusions.
- Confirmatory Data Analysis (CDA): the objective is to use the data to confirm or refute an existing hypothesis. It is particularly used in the scientific world.
- Qualitative Data Analysis (QDA): this type of analysis focuses on non-numerical data. QDA is mostly used in the social sciences.
Why use data analytics?
Traditionally, organizations carried out analytics for reporting purposes. The idea was usually to improve performance by measuring what had happened against set metrics. For example, what were monthly sales figures and how did they compare to targets?
Today data analytics can be used in many more ways, supporting data-driven decision making across the organization. To enable this it is essential to democratize analytics, by making reports, formats and data accessible and usable by everyone within the organization, whether they are experts or not.
Here are some concrete examples of analytics in action:
- Banks: using the data to limit fraud and identity theft, reducing risk and protecting customers.
- Ecommerce: analyzing user behavior to provide the best possible experience and therefore encouraging loyalty and conversions.
- Local government: reusing data to create new services for citizens, such as better waste management or applications that promote urban mobility.
These demonstrate that analytics is a practice that has multiple applications that go far beyond static reporting.
How to optimize data analytics?
Faced with increasing volumes of data, successful analytics is becoming a real challenge for many organizations. Here are some best practices to apply to optimize the entire process.
Gather all data
This is the first essential step – without data collection, there is no data analysis possible. Organizations must therefore put in place clear processes to encourage data collection by everyone, in every department; whether they are sales people in the field, administrative managers or data analysts. To ensure data is consistent and high quality it is vital to put in place a robust data governance policy.
Centralize data
Successful data analysis is built on access to high quality, reliable data. In order to make data accessible, organizations should implement a platform that centralizes all data, whether from internal or external sources. This way, all employees (and even third parties, if the data is opened) will easily find what they need by accessing a single place.
Use powerful tools
With the enormous volumes of data present in organizations today, human beings are no longer always able to analyze all the information at their disposal in a reasonable time. Therefore look at combining human action and technology such as AI to conduct efficient data analysis.
Keep your data up to date
For analysis to be reliable, data must be high-quality and consistent. As part of data governance, organizations should appoint data stewards, who are responsible for sorting and updating specific datasets.

Access to accurate statistical information is key to the successful functioning of the global economy and for policymakers and businesses to make informed decisions around subjects that impact us all. How can institutions effectively and efficiently share their statistical data in an interoperable, scalable way to democratize access and build trust?
Data portals need to demonstrate their impact and meet user needs by providing the right data assets to generate reuse. We explore how our customers are using the Opendatasoft data lineage feature to analyze portal performance and continually improve the experience they provide.
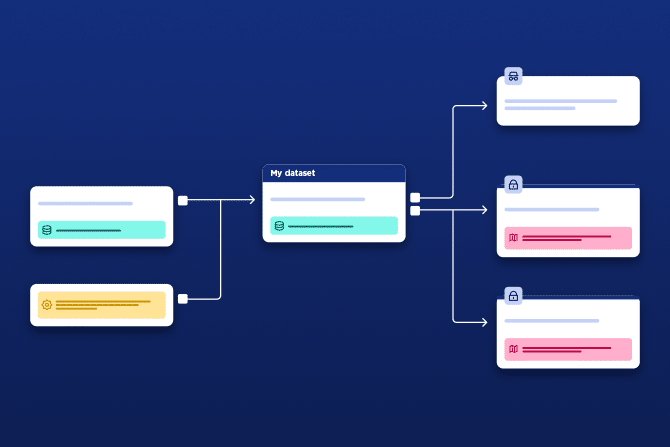
Opendatasoft has launched its unique, innovative data lineage feature. Focused on usage, it allows organizations to better understand how their data is used internally and externally, across data ecosystems, while improving the ease and efficiency of data portal management.
